
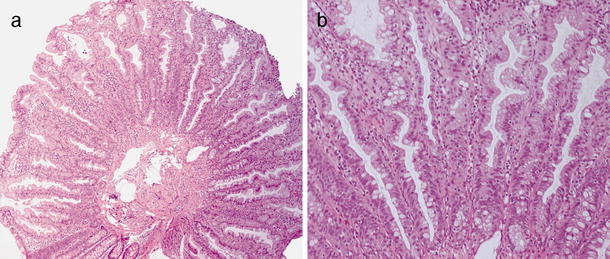
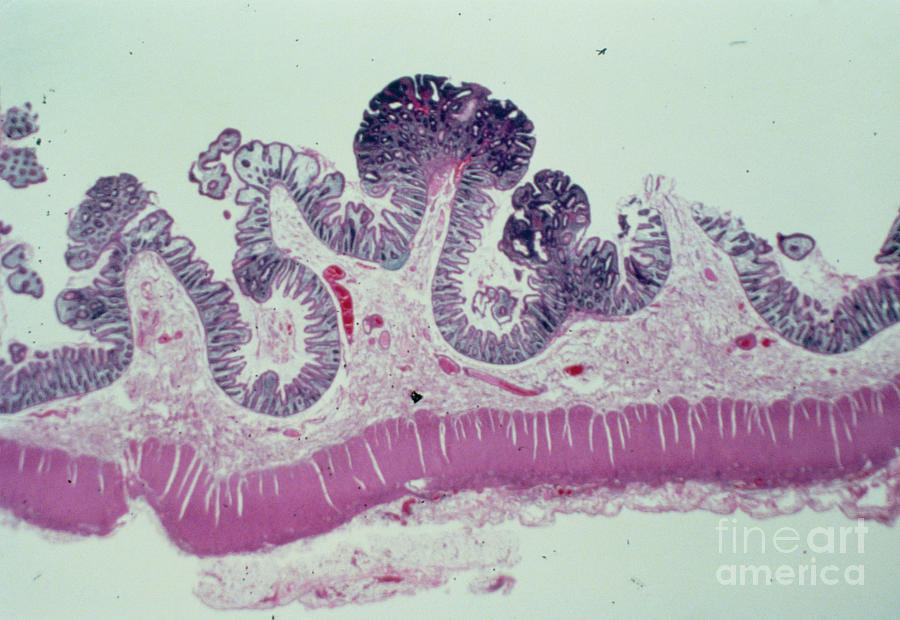
The architecture may be tubular, villous, or tubulo-villous. The adenomatous proliferation is characterized by different degrees of cell dysplasia ( atypia or loss of normal differentiation of epithelium) irregular cells with hyperchromatic nuclei, stratified or pseudostratified nuclei, nucleolus, decreased mucosecretion, and mitosis. Depending on the type of the insertion base, adenoma may be pedunculated (lobular head with a long slender stalk) or sessile (broad base). In hollow organs (digestive tract), the adenoma grows into the lumen - adenomatous polyp or polypoid adenoma. Histopathology Īdenoma is a benign tumor of glandular tissue, such as the mucosa of stomach, small intestine, and colon, in which tumor cells form glands or gland like structures. Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms. However, even though benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures ( mass effect) and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner (causing paraneoplastic syndromes). Over time adenomas may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Although adenomas are benign, they should be treated as pre-cancerous. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure (as can happen in familial polyposis coli). Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others.

Colorectal cancer screening: an updated review of the available options. Characteristics of and risk factors for colorectal neoplasms in young adults in a screening population.
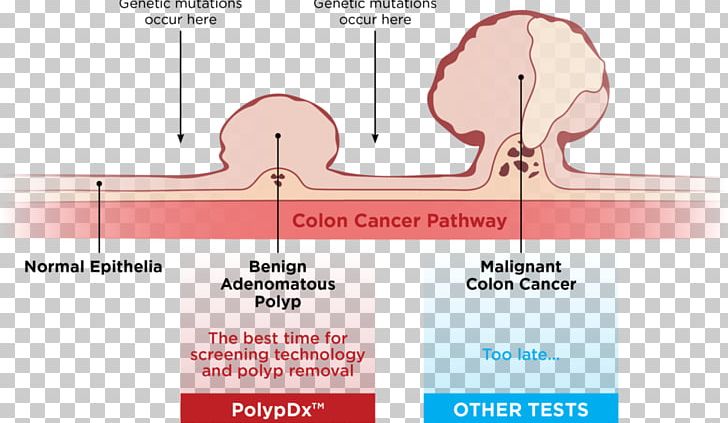
Lee SE, Jo HB, Kwack WG, Jeong YJ, Yoon YJ, Kang HW. Mutation analysis of adenomas and carcinomas of the colon: early and late drivers. Adenomatous polyposis syndromes: diagnosis and management.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
